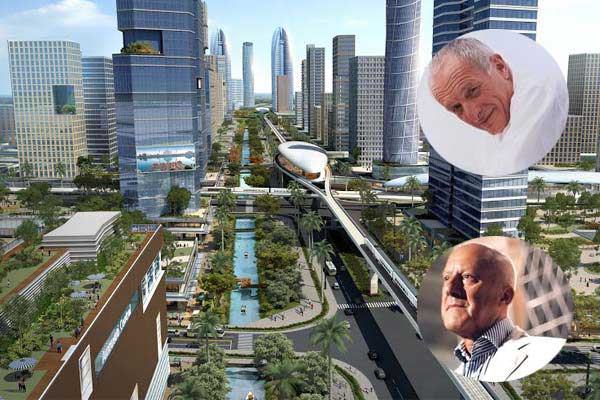
Chief minister Chandrababu Naidu seems to be keen on experimenting with high-tech architecture and natural light in the construction of capital Amaravati.
Today he had consultations with world’s most decorated architects in the field. Two architects of international repute in the field are in the race to bag the contract of designing the core capital of Amarvati. It is not clearly known, if they vie or unite to design the proposed capital city of Andhra Pradesh. Once friends and now competitors, Lord Norman Foster and Richard Rogers are in consultations with chief minister N Chandrababu Naidu. Recently they locked horns to get the contract of Taiwan International airport.
State government stared consultations with experts to give shape to the chief minister Naidu’s idea of Amaravati. Though the state government invited three experts, the third one Harry Cooler is unlikely to join. But the two architects, Lord Norman Robert Foster and Richard Rogers are said to have agreed to participate in the construction of Capital city. Lord Norman and Richard Rogers had a meeting with chief ministery N Chandrababu Naidu today in Vijayawada on Friday and discussed the various aspects of the Amaravati city.
Manchester born Norman Foster left school at 16, to work in the city’s treasurer’s office before going to be Manchester University’s School of Architecture and City Planning. In 1961 he won a fellowship to Yale University in USA, where he met Richard Rogers. The two set up in practice together in 1963 founding a firm called Team 4,with their respective wives of the time, Wendy Cheesman and Su Rogers. But, the Team 4 did not last more than four year. In 1967, Foster formed his own firm called ‘Foster and Partners’. Eschewing the usual Concrete shell favored by other architects, Foster uses modern materials , especially steel and glass and opted wherever possible natural light.
London’s British Museum, Berlin’s Reichstag, Beijing airport, Hearst Tower in New York are some of the most important structure where one can see signature of Foster (76). In 1999 he was awarded the Pritzker Architecture Prize, which is often referred to as the Nobel Prize of architecture. In 2009 Foster was awarded the Prince of Asturias Award in the Arts category. In 1994 he received the AIA Gold Medal. The Willis Faber and Dumas building in Ipswich, completed in 1974 was Foster’s big break. The first of many glass-sheathed office complexes , the building’s entrance featured two large escalators, a turfed roof garden and an Olympic sized pool in the basement.
Rogers studied at the Architectural Association in London (1954–59) and Yale University (1961–62). In 1977 Rogers created the Richard Rogers Partnership, a firm featuring some of the designers who worked on the Pompidou Centre. He gained more international attention for his spectacular Lloyds of London skyscraper (1978–86). Rogers’s work reached its greatest audience when he designed the Millennium Dome(1996–99) in Greenwich, England. Among Rogers’s later works is Terminal 4 (2005) at Madrid Barajas International Airport; the structure, which earned the Royal Institute of British Architects’ Stirling Prize in 2006, features an undulating roof and is noted for its use of light. Rogers received a number of other awards, including the Japan Art Association’s Praemium Imperial prize for architecture in 2000 and the Pritzker Prize in 2007. In 1995 he became the first architect to deliver the annual BBC Reith Lectures, a series of radio talks; these were later published as Cities for a Small Planet (1997). Rogers was knighted in 1991 and was made a life peer in 1996.