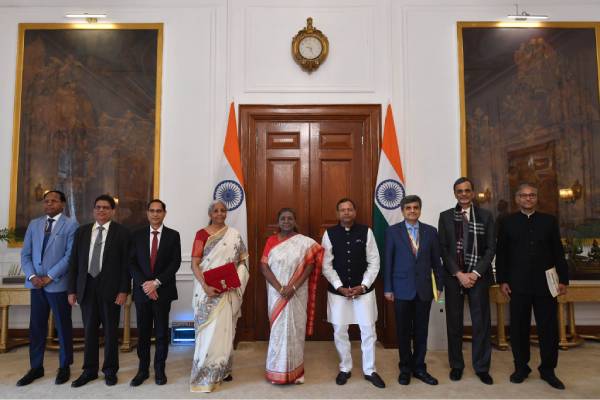
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2025-26, marking her eighth consecutive budget. This budget focuses on easing the financial burden on the middle class, boosting economic growth, and ensuring fiscal prudence. Here are the key highlights and announcements:
Key Announcements
1. Boost to Insurance and Infrastructure Sectors
FDI in Insurance: The FDI limit for the insurance sector has been raised to 100%, applicable to companies investing their entire premium in India.
Infrastructure Development: NABFID will set up a partial credit enhancement facility for infrastructure bonds.
Regulatory Reforms: A highlevel committee will be formed to streamline regulations in the nonfinancial sector.
State Investment Index: An investment friendliness index for states will be launched in 2025.
2. Focus on Bihar Ahead of Assembly Polls
Ahead of the Bihar Assembly elections, the Centre announced several initiatives for the state, including:
Establishment of a Makhana Board.
Development of greenfield airports.
A canal project in the Mithilanchal region.
3. Maritime and Tourism Development
Maritime Fund: A Rs 25,000 crore Maritime Development Fund will be established.
Tourism Push: Top 50 tourist destinations will be developed with PLIlinked incentives. MUDRA loans will be provided for homestays, and connectivity to hotel management institutions will be improved.
Medical Tourism: The “Heal in India” initiative will be promoted in PublicPrivate Partnership (PPP) mode.
4. Nuclear Energy Expansion
Nuclear Capacity: India aims to develop 100 GW nuclear capacity by 2047.
Small Modular Reactors: Five reactors will be operational by 2033, supported by a Rs 20,000 crore outlay.
5. UDAN Scheme Expansion
The government will launch a modified UDAN scheme to connect 120 new destinations, benefiting around 4 crore additional passengers over the next decade. The scheme will also focus on helipad operations in hilly regions and the North East.
6. Reforms in Six Key Areas
The budget introduces reforms in taxation, urban development, mining, the financial sector, power, and regulatory frameworks. The goal is to achieve inclusive growth and a “Viksit Bharat” with zero poverty, quality education, and affordable healthcare.
7. Manufacturing and Social Welfare
National Manufacturing Mission: This initiative will support cleantech and build ecosystems for solar cells, EV batteries, and highvoltage transmission equipment.
Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0: Nutritional support will be provided to 8 crore children.
Cancer Care: Daycare cancer centers will be established in all district hospitals within three years.
8. Education Sector Reforms
Atal Tinkering Labs: 50,000 labs will be set up in schools to foster scientific curiosity.
Broadband Connectivity: All government secondary schools will be provided with broadband connectivity.
Medical Education: 75,000 additional UG and PG medical seats will be added in the next five years.
9. Support for MSMEs
Credit Enhancement: Credit limits for MSMEs have been increased to Rs 10 crore.
FirstTime Entrepreneurs: Loans of Rs 2 crore will be provided to SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
10. Agriculture and Fisheries
Kisan Credit Card: The loan limit has been raised from Rs 3 lakh to Rs 5 lakh.
Fisheries Development: A focus on sustainable harnessing in Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep.
PM Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana: This initiative will cover 100 districts, benefiting 1.7 crore farmers.
11. Zero Income Tax for Income Up to ₹12 Lakh Under New Tax Regime
In a significant move aimed at providing relief to the middle class, the government has introduced sweeping reforms in the personal income tax structure under the new tax regime.
The highlight of these changes is the introduction of a ‘zero tax’ slab for incomes up to ₹12 lakh (₹12.75 lakh for salaried individuals, including a standard deduction of ₹75,000).